
For example, the two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C, have 6 and 7 neutrons, respectively. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. The isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.

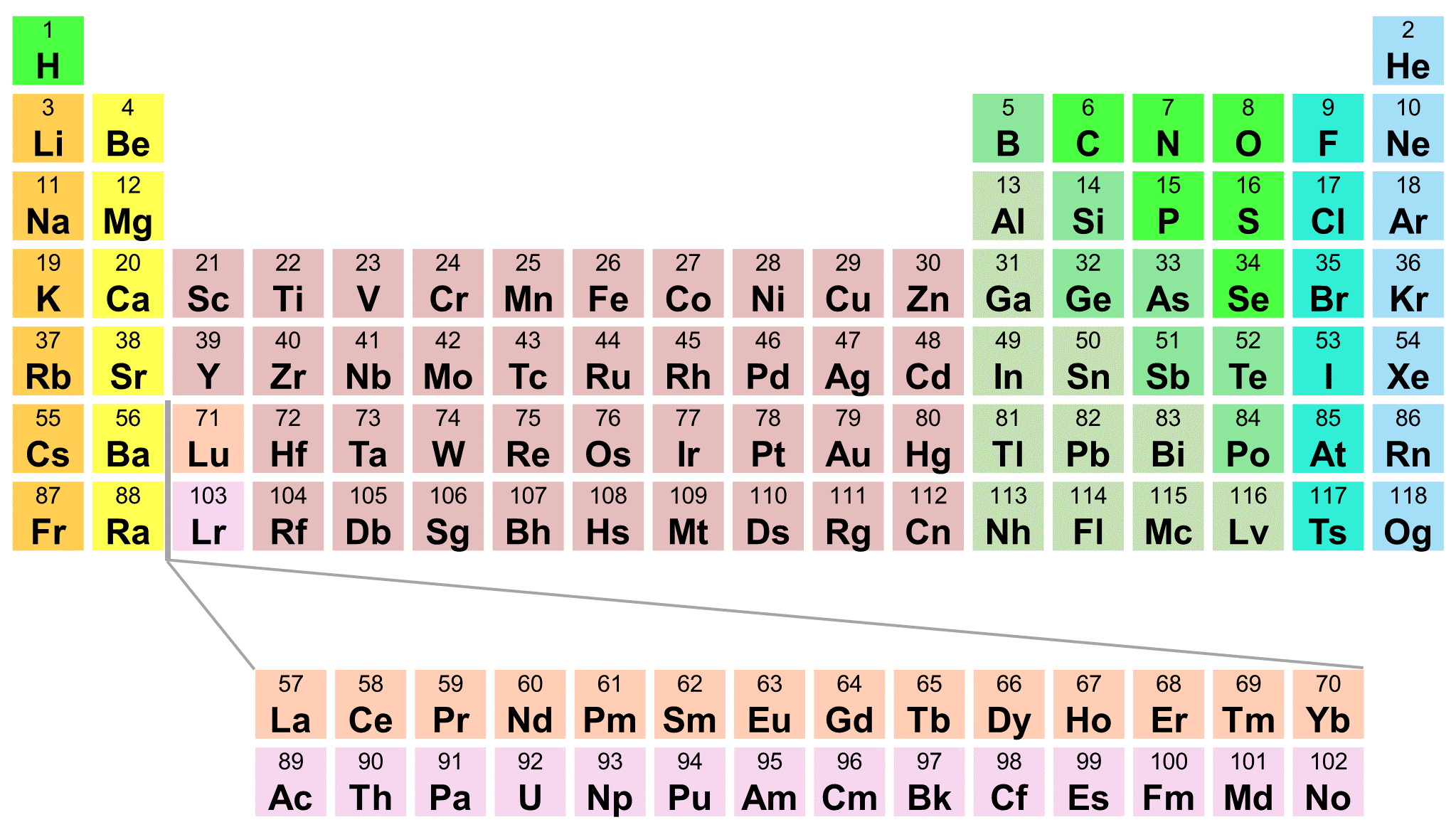
Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons. Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu), which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.Ītomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Boiling pointĪtomic number: The number of protons in an atom.

In a sorted list, these elements are shown before other elements that have boiling points >0☌. The density of elements with boiling points below 0☌ is given in g/l.List of Periodic Table elements sorted by → Atomic number No.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
